Venture Capital: Fuel for Startup Growth, How Does it Work
- Hammad Hasan

Venture capitalists (VC) plays a pivotal role in the startup ecosystem, providing crucial financial support to innovative companies in exchange for ownership stakes. If you’re an aspiring entrepreneur or simply curious about the world of startups, understanding venture capital is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of VC, exploring what it is, how it works, and why it’s such a driving force behind innovation and growth.
What Is Venture Capital
Venture capitalists are a form of private equity firm, whose investment focused on nurturing and funding early-stage, high-potential startups. Unlike traditional bank loans or other forms of financing, VC funding is typically provided by individuals or organizations known as venture capitalists. These investors are looking for promising businesses with the potential for rapid growth and a high return on investment (ROI).
Why Do Startups Seek Venture Capital?
Startups seek venture capital for several reasons:
Capital Infusion: VC funding provides the financial resources necessary to develop products, scale operations, and enter new markets.
Expertise and Mentorship: Venture capitalists often bring valuable industry knowledge and connections, guiding startups toward success.
Credibility: A venture capital investment can serve as a stamp of approval, making it easier for startups to attract additional investors, customers, and talent.
Exit Strategy: VC investors are motivated to help startups grow and succeed, as they aim to realize substantial returns when the startup goes public or gets acquired.
VC & Startup Investment Rounds
Venture capitalists invest in companies based on their predetermined goals, expected returns, and risk tolerance. Some VCs prioritize high liquidity, seek substantial returns, and are willing to invest in high-risk ventures. Conversely, others aim for lower risk and more modest returns. Additionally, startups require investment at various stages of their development, each of which has distinct names and significance, as explained below.
Seed Stage: The VC process usually begins at the seed stage, where a startup is just an idea or prototype. Founders approach venture capitalists with a business plan and pitch. If the idea is compelling, venture capitalists may offer funding to help the startup develop its product or service.
Early-Stage: As the startup progresses and shows promise, it enters the early-stage phase. At this point, venture capitalists inject more substantial amounts of capital into the company in exchange for equity. This funding helps the startup refine its product, build a team, and scale its operations.
Growth Stage: Once the startup has proven its viability and achieved significant growth, it enters the growth stage. Venture capitalists may provide additional funding to fuel expansion, marketing, and market penetration efforts.
Exit Stage: The ultimate goal of venture capitalists is to realize a return on their investment. This usually happens through an “exit event” such as an Initial Public Offering (IPO) or an acquisition by a larger company. When this occurs, venture capitalists sell their equity shares, reaping the rewards of their early investment.
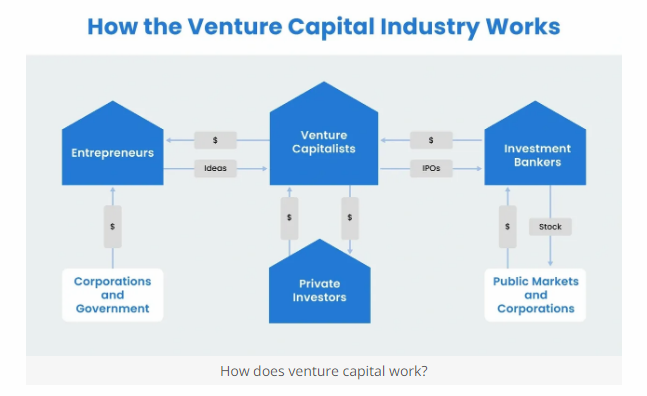
What is the Venture Capital Investment Process?
The venture capital (VC) investment process is a structured series of steps that venture capitalists follow when evaluating, selecting, and investing in startups or early-stage companies. This process ensures that both the venture capitalist and the startup make informed decisions and align their goals. Here’s an overview of the typical venture capital investment process:
Deal Sourcing:
Identification: Venture capitalists actively search for potential investment opportunities. These opportunities can come from various sources, such as referrals, networking events, pitch deck competitions, or submissions through the VC firm’s website.
Screening and Evaluation:
Initial Screening: VC firms conduct an initial assessment of the opportunities to determine if they align with their investment criteria. This includes evaluating the startup’s industry, market potential, team, and product or service.
Due Diligence: If the initial screening is favorable, a more thorough due diligence process begins. This involves in-depth research into the startup’s financial model, market dynamics, competitive landscape, legal and regulatory issues, intellectual property, and more. The goal is to identify potential risks and opportunities.
Term Sheet Negotiation:
Offer Letter: If the due diligence process is successful, the VC firm extends an offer in the form of a term sheet. The term sheet outlines the proposed terms and conditions of the investment, including the amount of funding, equity ownership, valuation, board representation, and any protective provisions.
Deal Structuring:
Legal Agreements: Once both parties agree to the terms outlined in the term sheet, they proceed to negotiate and draft legal agreements. These agreements include the investment agreement, stock purchase agreement, and any other necessary contracts.
Closing the Deal:
Signing: After the legal documents are finalized, both the startup’s founders and the venture capitalists sign them.
Funding: The venture capitalists transfer the agreed-upon funds to the startup. The funds are typically disbursed in tranches based on specific milestones or achievements.
Post-Investment:
Board Representation: Venture capitalists often secure a seat on the startup’s board of directors or advisory board, allowing them to have a say in the company’s strategic decisions.
Support and Mentorship: VC firms provide guidance, mentorship, and access to their network to help the startup grow and succeed.
Monitoring and Reporting: Venture capitalists closely monitor the startup’s progress, financial performance, Bookkeeping and Accounting, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Additional Funding Rounds: Depending on the startup’s growth and funding needs, subsequent rounds of financing may be considered in the future.
Exit Strategy:
Exit Event: Venture capitalists seek an “exit event” to realize a return on their investment. This can occur through an Initial Public Offering (IPO), acquisition by a larger company, or other strategic transactions.
Distribution of Returns: When the exit event occurs, the venture capitalists and founders share the returns based on the ownership structure and terms outlined in the investment agreement.
It’s important to note that the VC investment process can vary from one VC firm to another and may be influenced by factors such as the industry, investment stage, and the specific goals of the investors and founders involved. Additionally, startups should carefully consider the implications of accepting VC funding, as it often involves giving up equity and ceding some control over the company’s direction.
What Percentage of a Company Do Venture Capitalists Take?
The percentage of a company that venture capitalists (VCs) take in exchange for their investment varies widely and depends on several factors, including the stage of the company, its valuation, the amount of funding needed, and the negotiating leverage of the founders. However, there are some general guidelines and considerations to keep in mind:
Early-Stage vs. Later-Stage: In early-stage investments, such as seed or Series A rounds, VCs typically take a larger ownership stake because they are taking on higher risk. This percentage can range from 20% to 50% or more, depending on the specific circumstances. As the company progresses to later stages, VCs may take a smaller percentage as the valuation increases.
Valuation: The Company’s valuation at the time of the investment is a critical factor. If the company has a high valuation, VCs may accept a smaller ownership stake for their investment. Conversely, if the valuation is lower, VCs may require a larger ownership stake to justify their investment.
Amount of Funding: The amount of funding being provided by the VC also plays a role. In some cases, VCs may invest a relatively small amount and take a larger ownership stake, while in other cases, they may provide significant funding in exchange for a smaller percentage.
Negotiation: Negotiation skills and leverage play a significant role in determining the ownership stake. Founders who have multiple VC firms competing to invest in their company may have more negotiating power and may be able to secure a more favorable ownership arrangement.
Founder’s Equity: Founders typically retain a significant portion of equity in their company, even after VC investment. It’s not uncommon for founders to collectively retain 50% or more of the company’s ownership, especially in the early stages.
Investor Preferences: Some VC firms have specific ownership targets they aim for in their investments. These targets can vary widely between firms and may influence the ownership stake they seek.
Vesting and Equity Vesting: VCs often require that founders and key employees have vesting schedules in place. This means that ownership of their shares gradually accrues over time, typically over a four-year period with a one-year cliff. This ensures that founders are committed to the long-term success of the company.
It’s essential for founders and VCs to have clear and open discussions during the negotiation process to arrive at an ownership structure that aligns with the company’s growth plans and the expectations of both parties. While VCs do take ownership stakes in exchange for their investment, they also provide valuable expertise, resources, and support to help the company grow, making it a mutually beneficial partnership. The specific ownership percentage will vary based on the unique circumstances of each investment and the goals of the founders and investors involved.
Why Is Venture Capital Important?
Venture capital (VC) plays a vital and multifaceted role in the business and innovation ecosystem. Its importance stems from several key factors:
Funding Innovation: VC provides funding to early-stage startups with innovative ideas, technologies, and business models. This financial support is often unavailable through traditional sources such as bank loans, making it a crucial driver of innovation.
Support for Risky Ventures: Startups frequently face high levels of risk and uncertainty. Venture capitalists are willing to invest in these risky ventures, allowing entrepreneurs to pursue groundbreaking ideas without shouldering all the financial risk themselves.
Job Creation: Startups and high-growth companies that receive VC funding are significant contributors to job creation. They often hire talent at a rapid pace, stimulating economic growth and reducing unemployment.
Economic Growth: VC-backed companies can have a substantial impact on a region’s or country’s economy. They contribute to economic growth through increased tax revenue, business expansion, and the creation of ancillary industries and services.
Innovation Ecosystem: VC fosters a dynamic innovation ecosystem. It encourages the development of new technologies, products, and services, which can lead to industry disruption and improved quality of life.
Global Competitiveness: Venture capital enables countries to remain competitive on a global scale. It helps attract and retain entrepreneurial talent and encourages domestic innovation, which can lead to the creation of globally competitive companies.
Access to Expertise: Venture capitalists often have extensive industry knowledge and networks. Startups benefit not only from the funding they provide but also from the expertise, mentorship, and guidance these investors offer.
Long-Term Vision: While venture capitalists seek a return on their investment, they often have a longer-term investment horizon compared to traditional lenders. This allows startups to focus on growth and market share before prioritizing profitability.
Validation and Credibility: Securing VC funding can serve as a stamp of approval for a startup. It validates the viability of the business idea and can make it easier to attract customers, partners, and additional investors.
Diversification: For investors, venture capital provides an opportunity to diversify their portfolios. Investing in startups can yield high returns, potentially offsetting losses in other investments.
Technological Advancements: Many of the technological advancements and breakthroughs in various industries, including technology, healthcare, and biotechnology, have been made possible through VC-backed startups.
Spillover Benefits: The innovations and technologies developed by VC-backed companies often have spillover effects on other industries and sectors, leading to broader societal benefits.
Venture capital is a critical catalyst for innovation, economic growth, and job creation. It empowers entrepreneurs to pursue bold ideas, fosters a culture of innovation, and contributes to the development of game-changing technologies and businesses. The role of venture capital in nurturing the growth of startups and fostering economic prosperity cannot be overstated.
What Is the Difference Between Venture Capital and Private Equity?
Venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) are both forms of private investment, but they differ significantly in terms of their focus, investment stage, objectives, and the types of companies they typically target. Here are the key differences between venture capital and private equity:
Investment Stage:
Venture Capital: VC primarily focuses on early-stage and growth-stage companies, often startups. Venture capitalists provide funding to companies that are in their infancy or early stages of development, with the goal of helping them grow and achieve market success.
Private Equity: PE typically targets more mature companies that are well-established and have a proven track record of revenue and profitability. Private equity firms often acquire existing companies to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and enhance profitability.
Risk and Return Profile:
Venture Capital: VC investments are associated with higher risk due to the early-stage nature of the companies involved. However, they also offer the potential for substantial returns if the startup succeeds and experiences significant growth.
Private Equity: PE investments tend to have lower risk compared to VC investments because they involve established companies with a history of performance. The focus in private equity is often on achieving consistent, steady returns rather than rapid growth.
Ownership Stake:
Venture Capital: Venture capitalists typically take an equity ownership stake in the companies they invest in. This stake can range from a minority ownership position to a significant ownership share, depending on the stage of the company and the amount of funding provided.
Private Equity: Private equity firms usually acquire a controlling or majority ownership stake in the companies they invest in. They seek to have significant influence or control over the company’s operations and strategic decisions.
Investment Horizon:
Venture Capital: VC investments have a longer-term horizon, often ranging from several years to a decade or more. Venture capitalists expect to support the company through its growth stages until an exit event, such as an IPO or acquisition, provides a return on their investment.
Private Equity: PE investments typically have a shorter investment horizon compared to VC. Private equity firms aim to enhance the value of the acquired company within a few years and then exit with a profit, either through a sale to another entity or by taking the company public.
Objectives:
Venture Capital: The primary objective of venture capital is to fuel the growth and development of early-stage companies. VC firms are often willing to accept higher risks in exchange for the potential of substantial capital appreciation.
Private Equity: Private equity focuses on optimizing the performance of established companies, often through operational improvements, cost reductions, and strategic initiatives. The goal is to increase the company’s value and profitability.
Size of Investments:
Venture Capital: VC investments tend to be smaller in scale, typically ranging from a few hundred thousand dollars to several million dollars in early-stage rounds.
Private Equity: PE investments are generally larger, often involving millions or even billions of dollars, especially in the case of leveraged buyouts (LBOs) of larger companies.
In summary, venture capital and private equity are distinct forms of private investment that cater to different stages of a company’s lifecycle, have varying risk-return profiles, and pursue different objectives. VC focuses on nurturing startups and early-stage growth, while PE is concerned with optimizing the performance of established businesses. Both play crucial roles in the investment landscape and contribute to economic growth and innovation.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Venture Capital?
Venture capital (VC) is a crucial source of funding for startups and early-stage companies, but it comes with both advantages and disadvantages. Entrepreneurs and investors should carefully consider these factors before entering into a venture capital arrangement.
Advantages of Venture Capital:
Access to Capital: VC firms provide startups with substantial capital that is often difficult to obtain through traditional lending or other means. This funding can be used for product development, scaling operations, marketing, and more.
Expertise and Mentorship: Many venture capitalists have a wealth of industry knowledge and experience. They often take an active role in guiding and advising the startup’s management team, helping them navigate challenges and make informed decisions.
Networking Opportunities: Venture capitalists typically have extensive networks in the business world. They can introduce startups to potential partners, customers, and other investors, expanding the startup’s reach and opportunities.
Credibility: Securing venture capital funding can enhance a startup’s credibility. It signals to customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders that the company has been vetted by experienced investors and has the potential for success.
Risk Sharing: Venture capitalists share the risks of the startup. If the business fails, the founders are not personally liable for repaying the investment, as they would be with loans or personal investments.
Focus on Growth: VC-backed startups can focus on aggressive growth without the immediate pressure of profitability. This allows them to capture market share and establish a strong position in their industry.
Disadvantages of Venture Capital:
Loss of Control: One of the most significant drawbacks is the loss of control. Venture capitalists typically require equity ownership and may influence key decisions. Founders may have to give up a substantial portion of their company to secure funding.
High Expectations: Venture capitalists expect a high return on their investment, often within a relatively short timeframe. This can create pressure for rapid growth and may not align with the startup’s long-term vision.
Stringent Selection Process: VC firms are highly selective in choosing startups to invest in. Many promising companies are turned away, and the process can be competitive and time-consuming.
Exit Pressure: Venture capitalists expect an “exit event” where they can realize a return on their investment, typically through an IPO or acquisition. This can force startups to prioritize short-term gains over long-term sustainability.
Valuation Pressure: Startups that receive VC funding may face pressure to achieve high valuations in subsequent funding rounds, which can lead to overvaluation and unrealistic expectations.
Confidentiality Concerns: Sharing sensitive information with venture capitalists may raise concerns about confidentiality and intellectual property protection, particularly if the partnership doesn’t proceed as planned.
Potential for Conflict: Differences in vision and strategy can lead to conflicts between founders and venture capitalists, which can be detrimental to the company’s success.
In conclusion, venture capital can be a valuable source of funding and support for startups, but it also comes with significant trade-offs. Entrepreneurs should carefully consider their goals, the stage of their company, and their willingness to cede control and equity before pursuing VC funding. Additionally, finding the right venture capital partner who aligns with the startup’s vision and values is crucial for a successful and mutually beneficial partnership.
Risks and Rewards
While venture capital can be a game-changer for startups, it’s not without risks. Startups that accept VC funding typically relinquish a portion of ownership and control. Additionally, there’s no guarantee of success, and many startups fail despite VC backing.
On the flip side, successful VC-funded startups can achieve exponential growth and become industry giants. Notable examples include Google, Facebook, and Amazon, all of which received early-stage venture capital investments.
Case Study: Should this startup take VC money or Try to turn a profit?
The Bottom Line
Venture capital is a driving force behind innovation and entrepreneurial success. It provides startups with the financial resources, expertise, and credibility needed to thrive in a competitive business landscape. While it comes with risks, the rewards of VC funding can be extraordinary for both entrepreneurs and investors, fueling the growth of innovative companies that shape the future. As you embark on your entrepreneurial journey or seek to understand the startup ecosystem, venture capital is a concept you’ll undoubtedly encounter and appreciate for its role in fostering innovation and economic growth.