Solar power plants have emerged as a cornerstone of the renewable energy revolution, playing a pivotal role in combating climate change and fostering energy independence. With the global demand for clean and sustainable energy solutions surging, businesses, governments, and environmental advocates are increasingly prioritizing investments in solar technology. These investments aim to achieve ambitious sustainability goals, significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and transition away from reliance on fossil fuels.
For stakeholders such as investors, entrepreneurs, and energy providers, the potential of solar power is undeniable, but a critical question arises: What is the true cost of building a solar power plant, and how long does it take to achieve profitability? The financial and operational success of such a venture depends on multiple factors, including project size, location, technology selection, and financial incentives available.
This article provides a comprehensive examination of the key cost drivers, a detailed breakdown of initial investments, operational expenses, and revenue streams, as well as insights into the expected timeline for achieving profitability. Whether you are planning to install a small-scale system or undertake a large utility-scale project, understanding these details is essential for making informed decisions in the rapidly evolving renewable energy market.

Key Factors Influencing the Cost of a Solar Power Plant
Size and Scale of the Solar Plant
The size of the solar power plant significantly impacts its cost. Plants are categorized into:
Residential Solar Systems: Typically ranging from 5–20 kW and costing between $10,000 to $50,000.
Commercial Solar Systems: Usually between 50 kW to 1 MW, with costs spanning $50,000 to $1 million.
Utility-Scale Solar Farms: Ranging from several megawatts to gigawatts, costing between $1 million to $2 million per megawatt.
Larger systems benefit from economies of scale, reducing the per-watt installation cost compared to smaller systems.
Type of Solar Technology
There are two primary technologies used in solar power plants:
Photovoltaic (PV) Panels: These are widely used due to their lower costs and ease of installation. Prices for PV systems average $0.50 to $0.80 per watt.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): CSP systems are more expensive, ranging from $2.50 to $8 per watt, but they are often used for large-scale projects requiring energy storage.
Land Acquisition Costs
Land availability and costs vary significantly based on location. On average:
Urban Areas: Higher land costs due to scarcity and demand.
Rural Areas: Typically cheaper but may involve additional infrastructure expenses like access roads or transmission lines.
For utility-scale solar farms, approximately 5 acres are needed per megawatt of capacity, with land costs ranging from $1,000 to $10,000 per acre.
Installation and Construction Costs
Installation includes labor, equipment, and permitting fees. Labor-intensive activities like mounting panels, installing inverters, and connecting the plant to the grid can cost up to 30-40% of the total project expenditure. In developed countries, labor costs tend to be higher, pushing up installation expenses.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
Governments worldwide offer financial incentives to promote renewable energy:
Tax Credits: The Investment Tax Credit (ITC) in the U.S. allows up to 30% deduction on installation costs.
Subsidies: Some countries provide direct subsidies, further reducing capital expenditure.
Feed-in Tariffs (FiTs): Fixed rates paid for electricity generated by renewable sources can boost profitability.
Operational and Maintenance Costs
Solar plants require routine maintenance, including cleaning panels, checking inverters, and ensuring optimal performance. Annual O&M costs typically range between 1-3% of the initial investment.
Download the Ultimate Solar Plant Financial Model In Excel
Save over 40 hours of work with our expertly designed Solar Power Plant Financial Model Template, tailored to meet the needs of investors, entrepreneurs, and energy providers. This comprehensive tool includes 50+ critical assumptions covering investment, revenue, capacity, OPEX, CAPEX, and headcount projections. The model delivers a user-friendly and dynamic output, including:
Three Financial Statements (Income, Cash Flow, and Balance Sheet)
Cash Runway Analysis and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) of Solar Power Plant,
Investment Summary and Sensitivity Analysis
Working Capital Requirements and Advanced Valuation Methods i.e. DCF Valuation, Revenue Multiple & EBITDA Multiple Valuation
Equity Giveaway analysis & Burn Rate analysis
Whether you’re optimizing operations, preparing to present to stakeholders, or applying for SBA loans, this model ensures clarity and precision at every stage. Download now to accelerate your decision-making process and maximize your project’s potential!
Expected Timeline for Profitability of Solar Power Plant Project
The timeline for a solar power plant to achieve profitability is influenced by multiple factors, including upfront capital costs, energy production rates, revenue generation mechanisms, and financing arrangements. Understanding these elements is crucial for accurate financial forecasting, especially when using tools like a solar plant financial model in Excel or a solar startup financial model Excel template to evaluate project feasibility. Below, we break down the profitability timeline for different types of solar power systems.
1. Payback Period
The payback period is the duration it takes for a solar power plant to recover its initial investment through cost savings or energy sales. This metric is a cornerstone of any financial model for solar power plant projects, providing a clear projection of when profitability begins.
Residential Solar Systems: Typically, homeowners can recover their investment within 5–10 years, depending on the installation costs, local energy prices, and government incentives. Smaller-scale systems are generally quicker to pay off but may generate lower overall returns.
Commercial Solar Systems: Businesses implementing systems between 50 kW to 1 MW can expect a payback period of 8–12 years. These systems benefit from economies of scale and significant reductions in energy bills.
Utility-Scale Solar Farms: Large-scale farms ranging from several megawatts to gigawatts often have a payback period of 10–15 years. While the upfront investment is substantial, the long-term revenue potential from energy sales makes these projects highly lucrative over their lifecycle.
For precise calculations, leveraging a solar financial model Excel template can help predict break-even points based on input variables such as energy tariffs, operational costs, and financing terms.
2. Revenue Streams
Solar power plants generate revenue from diverse sources, and a well-prepared solar farm financial model Excel file accounts for these streams to maximize profitability. Key revenue channels include:
Selling Electricity:
A significant portion of revenue comes from Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), which provide fixed rates for selling electricity to utilities or end-users. These agreements ensure a steady income over the long term, essential for financial planning in projects modeled with solar PV financial model Excel templates.
Government Incentives:
Tax rebates, grants, and performance-based incentives can significantly offset initial costs. For example, the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) in the United States allows for a 30% deduction on installation expenses, which should be incorporated into the project’s financial model for solar power plant projects.
Energy Credits:
In markets where Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are tradable, plants can generate additional revenue by selling these credits to organizations aiming to meet renewable energy goals. Modeling these revenues in tools like a solar financial model Excel provides clarity on their impact.
3. Long-Term Profitability
Solar panels are designed to last 25–30 years, with annual efficiency degradation rates typically below 1%. After the initial payback period, the system operates at significantly reduced costs, allowing for substantial profitability during the remainder of its lifespan.
For instance, a solar plant financial model Excel can project annual cash flows, adjusting for declining panel efficiency while accounting for consistent operational and maintenance (O&M) costs. By year 10 or 15, the plant’s operational costs are often offset entirely by revenue, ensuring high margins for owners.
Detailed Cost Breakdown of a Solar Power Plant Project
To better understand the financial dynamics of solar projects, let’s examine the cost components of a 1 MW utility-scale solar power plant. These figures are essential inputs for any comprehensive solar farm financial model Excel sheet.
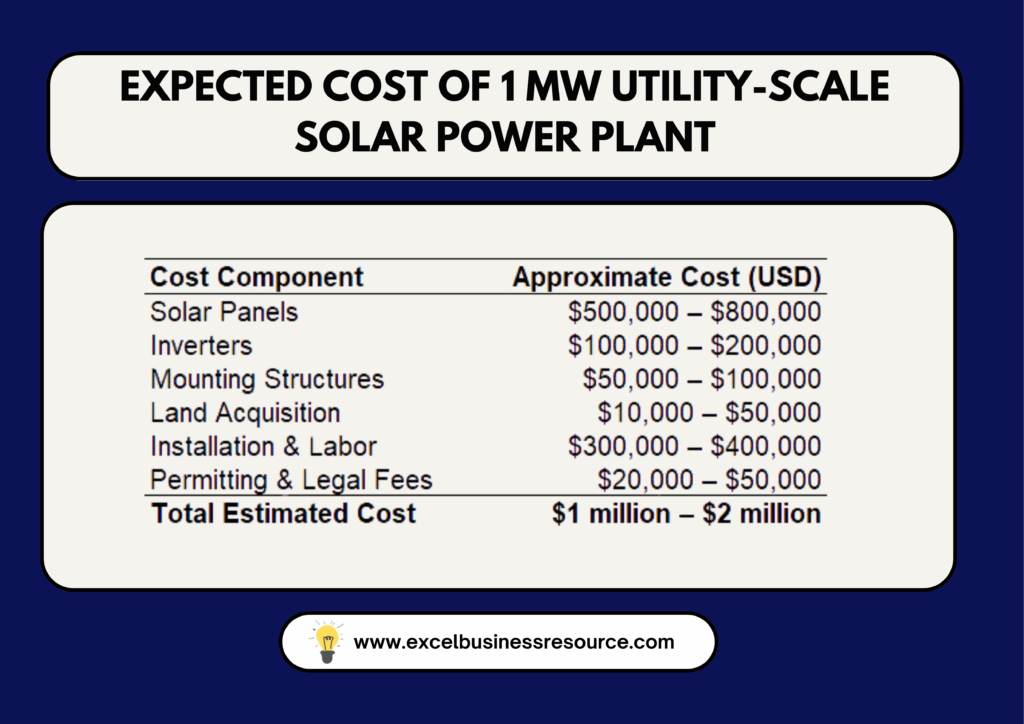
A dynamic financial model for solar power plant projects enables stakeholders to adjust these variables and test scenarios, ensuring accurate cost forecasting.
How to Optimize Costs and Maximize Profitability in Solar Farming
Achieving profitability faster requires careful planning and leveraging strategies that reduce costs and boost revenues. Here are key methods to optimize solar farming projects, which can be incorporated into a solar financial model Excel:
Leverage Economies of Scale
Scaling up projects reduces per-watt costs due to bulk procurement of materials and streamlined construction processes. Larger projects also tend to secure better financing terms, which can be factored into your solar PV financial model Excel file.
Choose Optimal Locations
Regions with higher solar irradiance generate more energy, increasing revenue potential. Locations with lower land costs can further reduce overall expenditure. By integrating geographic data into your solar farm financial model Excel, you can identify the most cost-effective sites.
Secure Government Incentives
Applying for tax credits, grants, and subsidies at both national and local levels can significantly reduce upfront capital requirements. Including these incentives in your solar financial model Excel helps project realistic payback periods and profitability timelines.
Adopt Advanced Technology
Investing in high-efficiency solar panels and incorporating battery storage systems can enhance energy production and allow for energy storage during peak hours, maximizing revenue potential. The additional costs and benefits should be reflected in the financial model for solar power plant projects (XLS).
Conclusion
Building a solar power plant is a significant investment, but the long-term financial and environmental benefits are undeniable. While upfront costs may seem daunting, strategic planning, government support, and proper financial modeling ensure profitability within a reasonable timeframe. The shift to renewable energy is not just a sustainable choice; it’s a lucrative one.