Running a Software as a Service (SaaS) startup is like steering a ship through ever-changing waters. To chart the course ahead, you need a reliable compass—accurate revenue forecasting. Whether you’re a seasoned founder or just launching your first SaaS venture, nailing your revenue predictions is critical to staying afloat and thriving. It’s not just about crunching numbers; it’s about understanding your business inside out, tapping into solid data, and using the right strategies to anticipate what’s next.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through the ins and outs of forecasting SaaS revenue like a pro. From decoding your business model to building financial models that hold up under pressure, we’ll cover a clear, step-by-step approach to fuel your growth. Whether you’re refining your pricing, hiring smarter, scaling strategically, pitching to investors, or just trying to get a clearer picture of your financial future, this roadmap will help you navigate with confidence. So, grab a coffee, and let’s dive into the world of SaaS revenue forecasting.
Written by Hamamd Hasan, a SaaS finance consultant with 5 years of experience guiding startups to multimillion-dollar ARR.
What Is SaaS Revenue Forecasting, and Why Should You Care?
SaaS revenue forecasting is the art and science of predicting future sales and income for a subscription-based software company. Unlike traditional businesses that rely on one-off sales, SaaS companies thrive on recurring revenue, which brings unique challenges and opportunities to the forecasting table.
How SaaS Forecasting Stands Apart
SaaS forecasting isn’t your grandpa’s sales projection. It’s tailored to the subscription model, and here’s what makes it different:
- The Power of Recurring Revenue
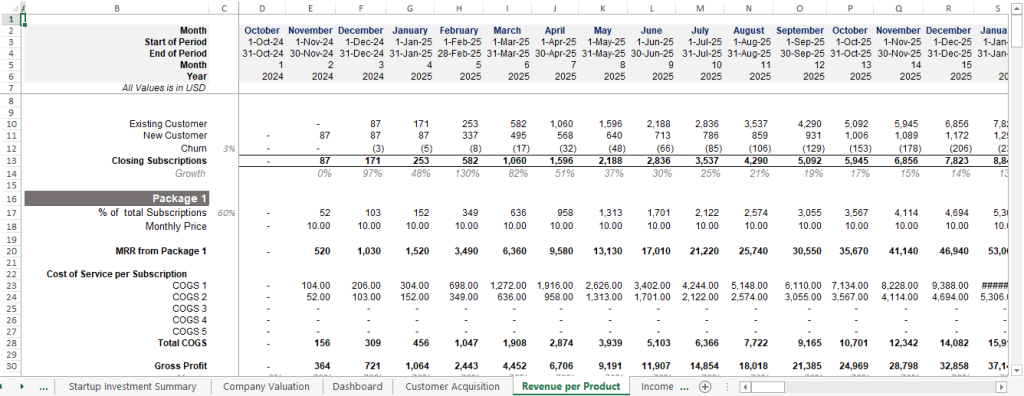
SaaS businesses live and breathe subscriptions, generating steady streams of monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and annual recurring revenue (ARR). While traditional businesses might focus on a single sale, SaaS forecasting hinges on these predictable, ongoing payments. Think of it like a gym membership versus selling a treadmill—one keeps paying, the other doesn’t.
- Churn: The Silent Revenue Killer
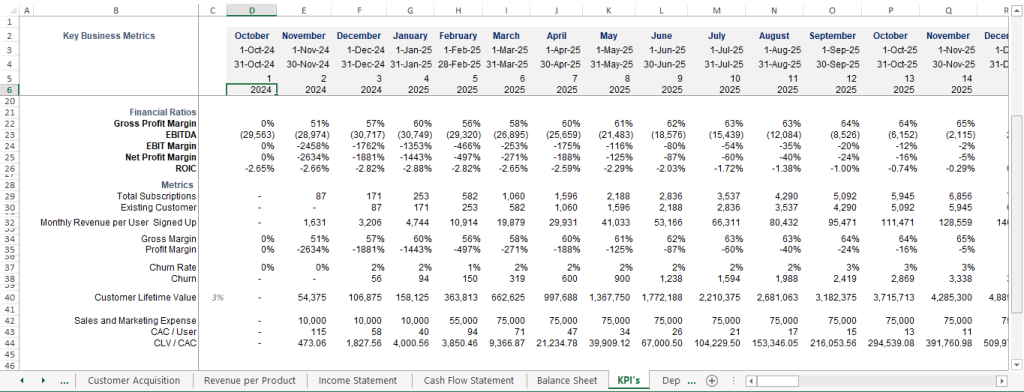
Churn rate—the percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions—is a make-or-break metric for SaaS. Recent data shows B2B SaaS companies face annual churn rates of 3-5% in 2025, with consumer-focused firms sometimes hitting higher. Traditional businesses might not sweat customer retention as much, but for SaaS, keeping churn low is a lifeline.
- Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC): The Price of Growth
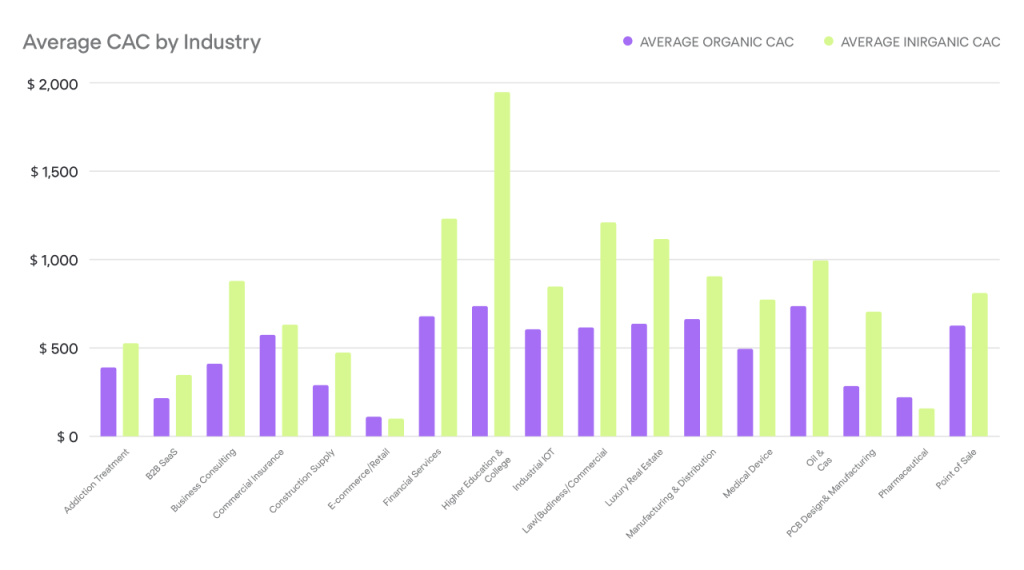
SaaS forecasting weighs the cost of acquiring customers (CAC) against their customer lifetime value (CLV). For example, fintech SaaS might spend $14,000 to land an enterprise client, while consumer SaaS averages under $300. Traditional models might focus on upfront sales costs, but SaaS tracks long-term acquisition efficiency.
- Expansion Revenue: The Hidden Gem
Upsells, cross-sells, and add-ons from existing customers can supercharge revenue. Forecasting these requires understanding user behavior, unlike traditional models that lean on one-time purchases.
- Usage-Based Pricing: A Moving Target
Some SaaS companies charge based on how much customers use their software, like cloud storage providers. Predicting usage patterns adds complexity compared to the fixed pricing common in traditional businesses.
- Runway: How Long Can You Last?
SaaS startups often burn cash early to fuel growth. Forecasting your runway—how long your funds will last—is as crucial as revenue projections. A Startup Runway Template can help you map this out alongside your revenue forecasts, a tactic useful for any business model.
Why does this matter? Accurate forecasting keeps you prepared for storms, aligns your team, and helps you make bold, informed decisions to grow your SaaS empire.
The Hurdles of SaaS Revenue Forecasting
Forecasting SaaS revenue is like solving a puzzle with moving pieces. It’s essential for planning, but challenges can throw you off course. Here’s what you’re up against and how to tackle them.
- The Rollercoaster of Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
CAC can swing wildly based on marketing strategies, competition, or market shifts. For instance, a spike in ad costs due to new players in your niche can inflate CAC. In 2025, SaaS companies spend about $2 on sales and marketing for every $1 of new ARR. Healthcare SaaS often faces steeper costs due to tricky targeting.
Tip: Test multiple acquisition channels and use A/B testing to stabilize CAC.
- Churn’s Unpredictable Sting
Churn varies with customer satisfaction, competitor moves, or shifting needs. In competitive markets, churn can spike above the 3-5% industry average. Tip: Invest in customer success teams and proactive retention strategies, like personalized onboarding.

- Market Swings and Seasonal Waves
Economic shifts or seasonal trends can disrupt demand. Retail SaaS might boom during holidays but dip in off-seasons.
Tip: Monitor market signals and build flexible models to account for these fluctuations.
- Product and Pricing Shake-Ups
New features or pricing changes can boost growth but muddy forecasts. When Salesforce rolls out updates, it must predict adoption rates to adjust projections.
Tip: Pilot pricing changes with a small segment to gauge impact before full rollout.
These hurdles demand sharp data, constant vigilance, and a willingness to adapt.

Proven Methods for SaaS Revenue Forecasting
Forecasting starts with solid data—your past and present performance are your crystal ball. Here are six methods to project your future, each with unique strengths.
Bottom-Up Forecasting
Perfect for new SaaS startups with no track record. Start with your team’s capabilities, your product’s unique value, and your target market’s demand. Estimate market size and build projections from the ground up. Example: A CRM startup might assume 100 new customers at $50 MRR based on early demos and market research.
Time-Series Analysis
Look at historical sales to spot trends, like seasonal spikes or steady growth. This works best for short-term forecasts but may miss external shifts.
Customer-Based Forecasting
Focus on customer metrics: acquisition rates, churn, and CLV. For instance, if you acquire 50 customers monthly with a $1,000 CLV and 4% churn, you can model future revenue.
Market Segmentation Analysis
Break your market into segments (e.g., small businesses vs. enterprises). Forecast each separately to pinpoint growth opportunities.
Predictive Analytics
Use machine learning to analyze big data for hidden patterns. Tools like Gong or Clari can predict customer behavior with scary accuracy.
Rolling Forecasting
Update forecasts monthly or quarterly to stay nimble. This helps you pivot when trends shift.
Method | Strengths | Weaknesses |
Bottom-Up | Great for startups | Relies on assumptions |
Time-Series | Spots trends | Misses external factors |
Customer-Based | Customer-focused | Needs robust data |
Market Segmentation | Targeted insights | Complex to execute |
Predictive Analytics | High precision | Requires tech expertise |
Rolling | Adapts quickly | Ongoing effort |
10 Best Practices to Nail SaaS Revenue Forecasting
Here’s how to make your forecasts accurate and actionable:
- Dig Into Historical Data: Spot patterns in past sales to ground your predictions.
- Know Your Business Inside Out: Master metrics like CAC, CLV, and churn to tailor your approach.
- Mix Forecasting Methods: Combine time-series and customer-based methods for a fuller picture.
- Stay Market-Savvy: Track competitors and trends. The SaaS market is expected to hit $408 billion in 2025.
- Check Your Work: Compare actual sales to forecasts monthly to refine accuracy.
- Segment Your Predictions: Break forecasts by customer type or product for sharper insights.
- Team Up Across Departments: Get input from sales, marketing, and product teams for a 360-degree view.
- Lean on Data Insights: Use analytics tools to uncover trends you might miss.
- Plan for What-Ifs: Model best, worst, and likely scenarios. For example, chart the impact of a 10% churn increase.
- Keep Improving: Treat forecasting as a living process. Learn from mistakes and adapt to new realities.
Want to put these into action? Download our SaaS Financial Model Templates to streamline your forecasting.
By following these best practices for SaaS revenue forecasting, you can develop more accurate, insightful, and actionable forecasts that drive success and unlock growth opportunities for your SaaS business.
Wrapping Up
SaaS revenue forecasting isn’t just number-crunching—it’s a strategic tool to boost cash flow, profitability, and valuation while making your business irresistible to investors. We’ve explored the process, dissected key methods like time-series and predictive analytics, and shared practical tips to get it right.
With these strategies, you’re ready to build a forecasting model that drives your SaaS forward. What’s your biggest forecasting challenge? Drop a comment below, and let’s keep the conversation going.
Hammad Hasan has prepared multiple SaaS financial forecasting models that helped companies to grow over $100M ARR.